In a recent study, it was found that an average human ingests and inhales 20 kg of Microplastics in their lifetime. That works out to 5 gm a week! On average, 45000 particles of Microplastics are ingested and 74000 particles are inhaled in the year. Surprised? It is presumed that the rate of intake will keep increasing every year as our dependence on plastics increases. The only good part is that presently an average Indian uses 11 kg of plastic per year whereas an average American consumes 109 kg per year.
Size Matters
To know more about plastic consumption, we first need to know that scientists have divided the plastics inside our body into two types depending on their size-
- Microplastics or MP and
- Nanoplastics or NP
The MPs are less than 5 mm in length and NP are less than 0.001 mm in length. These may seem like tiny amounts, but they can cause enough damage when they accumulate in the human body.
Ways of Entering Human Body
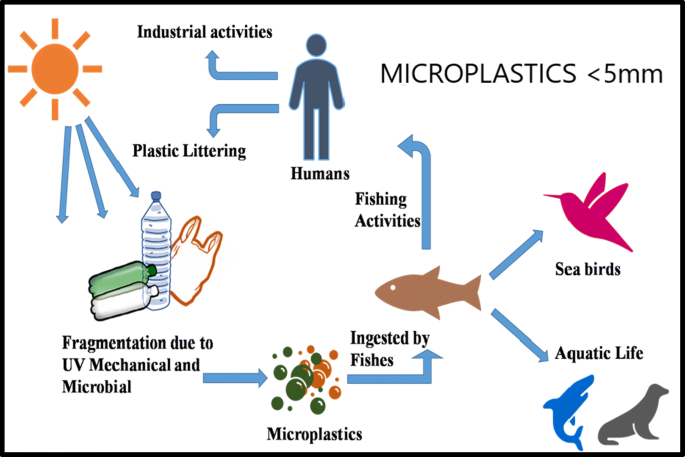
Plastics can enter the human body by three mechanisms: Food, Liquids and Air.
- Food – Earlier it was thought that seafood ingestion was the main source of MP and NP. Later all types of fish, meats, vegetables and fruits were found to have plastics. Not only food, even our toothpastes contain plastic.
- Liquids – All liquids including tap water, every where, have plastic in them. Be it mineral water, beer or juices, every liquid we consume has some amount of plastic. In a controlled study in US it was found that even rain water has plastic.
- Air – The air we breathe has varying amounts of plastic. Air, even in gardens or forests has some amount of plastic, carried by wind current.
Plastics and Chemicals
It’s not just the many different types of plastic we consume. Along with the plastics, are the chemicals that have leached into it. The chemicals vary with the type of products manufactured by the factories. So many types of plastics and so many chemicals, the scientists do not know enough of their effects.
Toxicity of Plastics in Human Body
Studies in this area are still in their nascent stages but the below facts have been established:
- Toxicity in human body may be of many types depending on the kind of plastic and chemical attached to it.
- Secondly, the accumulation of plastics in organs which try to filter them out like liver and kidneys may cause more damage.
- Thirdly, our lymphatic system which tries to scavenge and remove these toxins may themselves get affected.
- Fourthly, sensitive organs like brain may get damaged even by minute quantities of toxins.
- Some other organs may react by turning cancerous.
- Hormonal changes especially reproductive hormones may also occur.
The above has been studied in smaller marine and other animals. Studies in human donated cadavers are also in progress.
Few Disturbing Microplastic Facts
1. Bottled water contains 22 times more microplastics than tap water. A person who consumes only bottled water would consume 1,30,000 particles per year from this source alone as compared to 4000 particles per year from tap water.
2. More microplastics are leached out from plastic containers. Thus, storing cold food items in plastic containers/ packets may be safer but heating them in microwaves would release thousands of microplastics in our food. Switching over to glass containers is a much better idea.
3. Similarly, steaming plastic baby milk bottles during sterilisation or adding hot milk will leach out tremendous amounts of microplastics. Beware.
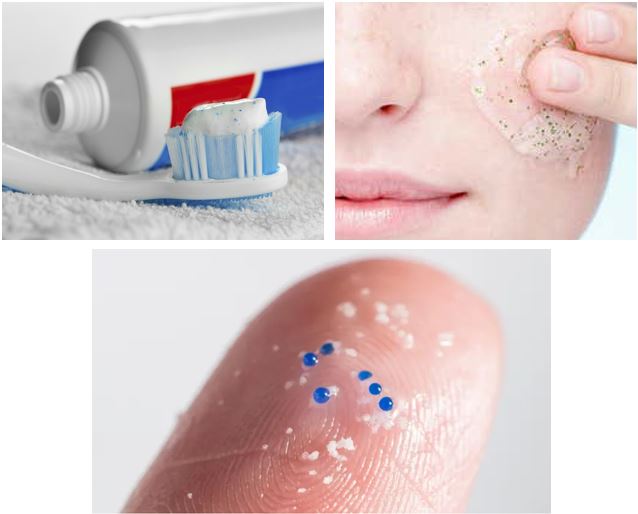
4. Microplastic beads have been used in many personal use items for whitening purposes. Toothpaste, face creams and even compact talcum for the face. They are no longer used by most manufacturers but their illegal import cannot be ruled out. These can easily enter our body through the mouth or our nose.
5. Entry of microplastics during steam inhalation or during facial steaming from electro- plastic gadgets also remains a risk. Steam inhalation from a stainless steel container may be cumbersome but a better idea.
6. Synthetic Clothing, bed linen and curtains. Synthetic is long-lasting, has a better sheen and does not require ironing. However, microfibres containing plastics come out with every wash and enter our water system. Hence, they need to be avoided.
Good News
Is there any good news? Yes! Scientists are discovering animal and plant life that devour microplastics. These are yet in the experimental stage and may take a few years to put in commercial usage.
- Micro algae. A micro algae has been discovered which can produce enzymes which degrade microplastics very fast.
- Crustacean. A crustacean has been discovered in Ireland which converts microplastics into nanoplastics in less than 100 hours.
- Larva. A species of a parasite on beehives has larvae which can degrade microplastics.
Bottom Line
When plastic was invented and innovated for a cheap, versatile item, it was never thought that we would be eating, drinking and breathing plastic. Until the rapid degradation of plastics without the release of Greenhouse Gases starts, we have to continue exercising the 3 R’s – Reduce, Reuse and Recycle. People have added 2 more – Refuse (plastic bags, plastic coverings, items that you don’t ‘need’) and Rot (Buy materials that can rot in nature and try to compost them).

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by the author do not necessarily reflect the views of the Government of India and Defence Research and Studies
Title Image Courtesy: Youtube
Article Courtesy: https://genkris.wordpress.com/2021/11/21/piling-of-plastic-in-human-body/