“Tolerance of intolerance enables oppression.” (DaShanne Stokes). These words speak volumes about the condition of the world today. Despite having International Laws related to the protection of Human Rights and many organisations for enforcing the same, unabated state-supported violations continue and have become a perineal problem for the world.
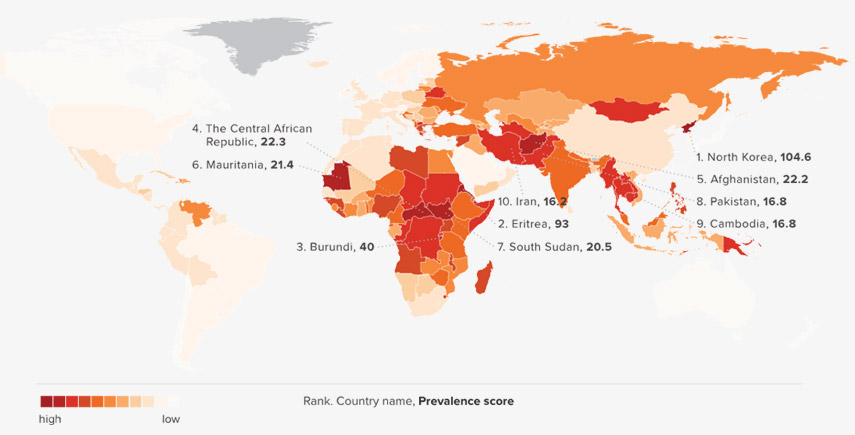
The world always hears a big hullabaloo by Pakistan, against Human Rights violations by India. Unfortunately, Pakistan is grossly affected by a classic syndrome termed in Hindi as “Diye Tale Aandhera” (Darkness beneath the lamp). It is interesting to note that according to a report (1) Pakistan is one of the 10 countries with the highest prevalence of modern slavery.
The article would be covered in following segments:-
- Human Rights & International Bill of Human Rights
- United Nations Human Rights Commission & its broad charter
- Pakistan and analysis of its Human Rights Compliance Record
- Oppression of Ethnic Minorities
- An area-specific analysis covering Baluchistan & Sindh
- Pakistan’s False Propaganda & its implications for India

1. Concept of Human Rights & International Bill of Human Rights
Human rights (2) are rights people have simply because they exist as human beings – they are not granted by any state. These universal rights have been historically considered inherent to all people regardless of nationality, sex, national or ethnic origin, colour, religion, language, or any other status. These range from the most fundamental – the right to life – to those that make life worth living, such as the rights to food, education, work, health and faith.
The International Conference (3) on Human Rights, which met at Teheran, from 22 April to 13 May 1968, to review the progress made in the 20 years since the adoption of the Universal Declaration and to formulate a programme for the future, solemnly declared in the Proclamation of Teheran.
The International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination as well as other conventions and declarations in the field of human rights adopted under the auspices of the United Nations, the specialized agencies and the regional intergovernmental organizations, have created new standards and obligations to which States should conform; It was a momentous achievement.
2. United Nations Human Rights Commissions (UNHRC) & It’s Charter UNHRC (4)
The U.N. General Assembly established the Human Rights Council in 2006 to replace the Commission on Human Rights. It is generally agreed that the Council is an improvement over the previous commission.
- Mandate and Role in the U.N. System
The Council has responsibility for “promoting universal respect for the protection of all human rights and fundamental freedoms for all.” It aims to prevent and combat human rights violations, including gross and systematic violations, and to make recommendations thereon; it also works to promote and coordinate the mainstreaming of human rights within the U.N. system. As a subsidiary of the General Assembly, it reports directly to the Assembly’s 193 members. It receives substantive and technical support from the U.N. Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR)(5)an office within the U.N. Secretariat.
Both the High Commissioner and the Office (OHCHR)(5) have a unique role to:
- Promote and protect all human rights
- Help empower people:
- Assist Governments:
- Inject a human rights perspective into all UN programmes:
3. Pakistan & its Human Rights Compliance Record in General
Unfortunately, Pakistan’s Human Rights compliance record has been quite dismal. Analysis of various reports/articles has shown that Pakistan has chosen to neglect even basic tenets of Human Rights and by far has consistently ignored UNHRC recommendations.
It has been reported (6) that Prime Minister Imran Khan’s government and the security services have cracked down on critical voices including journalists, activists, nongovernmental organizations, and the political opposition. The federal government has failed to mitigate the economic impact of Covid-19 on low-income workers and other vulnerable groups. Blasphemy-related violence, arbitrary detentions and extrajudicial killings by law enforcement agencies have been continuing with impunity.
Specific Accounts of Violations
A Human Rights Watch report (7) has clearly brought out areas where Pakistan has been found culpable:-
- Freedom of Expression and Attacks on Civil Society
- Freedom of Religion and Belief
- Women’s and Children’s Rights
- Terrorism, Counterterrorism, and Law Enforcement Abuses
- Death Penalty
- Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity
- Attacks on Health Workers
International Violations
The biggest matter of concern has been a report (7) that Pakistan and China deepened extensive economic and political ties in 2019, and work continued on the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, a project consisting of the construction of roads, railways, and energy pipelines. As a quid-pro-quo action, Pakistan taking along more than a dozen Muslim majority countries, signed a letter supporting China’s policies in Xinjiang that ignored widespread repression of the region’s Muslims.
Historically tense relations between Pakistan and India deteriorated further following a suicide bomb attack on a convoy of security vehicles in Pulwama in Jammu and Kashmir. Pakistan-based Islamist militant group Jaish-e-Mohammed claimed responsibility for the attack.
4. Oppression of Minorities (8)
The plight of Pakistani minorities was highlighted as the European Organisation for Pakistani Minorities organised a side event during the 33rd Session of the Human Rights Council in Geneva, Switzerland. The event highlighted the dire situation of many groups in Pakistan, including the Baloch, Gilgit Baltistan and Sindh communities, with an outlook to help the international community recognise the urgent need for reforms to help them.
It is opined that it is high time the international community take note of these violations and sets in motion processes to force Pakistan to honour its commitments to Protection of Human Rights,
5. Pakistan – Area Specific Analysis
- Baluchistan (9)
The Human Rights Commission of Pakistan (HRCP) has over the years condemned the Pakistan state for its dismal record in handling the cases of enforced disappearances in Baluchistan and hinted at the involvement of state agencies in such cases. Media personalities taking up this issue have also been coerced into silence.

The Baloch have argued that the Baloch people have always been cheated out of their resources and never been consulted when the decision to build the port was taken and that a major part of the revenue from it would fill the coffers of the central government while the province will receive only a minor share of it.
- Sindh Region (10)
This information has been culled out from the World Sindhi Congress (WSC) report (10). Sindh forms a province in south-eastern Pakistan, bordering the Pakistani provinces of Punjab and Baluchistan to the north and the west and the Indian states of Rajasthan and Gujarat to the east and southeast.

The report also stated that the minority communities’ especially Hindu minority has been particularly affected by oppressive national laws and discrimination – the application of blasphemy laws, for example, reveals the level of institutionalization of discrimination in the country The minorities have also been ruthlessly subjected to the forced conversions.
6. False Propaganda by Pakistan & its Implications for India (11)
There has been a sharp increase in Pakistan’s vicious information war campaign against India. An analysis would reveal three triggers: The Balakot attack of February 2019, the return of the BJP government in the May 2019 elections and the August 2019 revision of Article370.
Deoshar has rightly pointed out that these developments seem to have forced Pakistan to shift the emphasis of its anti-India strategy from fomenting terrorism supported by an information war component to an information war supported by terrorism & false implication of India for Human Rights Violations.
The key platforms for this strategy are Twitter, WhatsApp, YouTube and Facebook. Internal developments and dissent in India have been manipulated, packaged and used to develop a narrative damaging India’s social fabric. Key themes include India disenfranchising Muslims, and the “fascist Indian government’s” Hindutva supremacist ideology.
For India, there has to be a relentless vigil and battle against this campaign just as there has been against terrorism fomented by Pakistan. Even though the Indian polity is strong, such persistent venomous attacks can damage India’s social fabric and malign its image in the global arena affecting India both socially & economically. India should not allow itself & its polity, wittingly or unwittingly, to fall prey to such machinations to polarise society, even temporarily.
Conclusion
Tolerance of intolerance enables oppression.” (DaShanne Stokes). These words speak volumes about the condition of the world today in relation to Human Rights violations. Pakistan has been one of the 10 states cited by the United Nations for gross violations of Human Rights.
Human rights (2) are rights people have simply because they exist as human beings – they are not granted by any state. These range from the most fundamental – the right to life – to those that make life worth living, such as the rights to food, education, work, health and faith.
United Nations Human Rights Commission (UNHRC) and Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) have been trying to enforce protection of the Human Rights world over albeit with limited success.
Pakistan, which loudly tom-toms about Violation of Human Rights by India, has itself been a worst protractor of Human Rights violations, as per the UNPO reports. Pakistan has also joined hands with China and likeminded Islamic counties to suppress the revolt, by the Minority communities against Human Rights violations.
There has been a sharp increase in Pakistan’s vicious information war campaign against India. For India, there has to be a relentless vigil and battle against this campaign just as there has been against terrorism fomented by Pakistan. . India should not allow itself & its polity, wittingly or unwittingly, to fall prey to such machinations to polarise society, even temporarily.
Jai Hind
References:
- Countries that Violate Human Rights, ITMUSTBENOW, Retrieved from:https://www.itmustbenow.com/feature/our-big-questions/countries-violate-human-rights/
- What are human rights?, United Nations Human Rights-Office of the High Commissioner, Retrieved from https://www.hrw.org/world-report/2020/country-chapters/pakistan
- Fact Sheet No. 2 (Rev.1), The International Bill of Human Rights, June 1996, No. 2 (Rev.1), https://www.refworld.org/docid/479477480.html
- The United Nations Human Rights Council: Background and Policy Issues, https://fas.org/sgp/crs/row/RL33608.pdf , Title page 2 and Pages 2& 3
- About us OHCHR.org, https://www.ohchr.org/EN/AboutUs/Pages/WhoWeAre.aspx
- Pakistan, Human Rights Watch, https://www.hrw.org/asia/pakistan,
- World Report 2020-Pakistsn, 2020, Human Rights Watch, Retrieved from https://www.hrw.org/world-report/2020/country-chapters/pakistan
- Oppression of Ethnic Minorities in Pakistan https://unpo.org/article/
- Abysmal Human Rights Situation inBalochistan, https://idsa.in/idsacomments/abysmal-human-rights-balochistan-nazir-300520
- FORCED CONVERSION OF MINORITY GIRLS AND WOMEN IN PAKISTAN, https://unpo.org/downloads/2075.pdf ,Pages 3 to 9
- Pakistan’s information war campaign againstIndia needs attention, Indian Express, Retrieved from: https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/india-pakistan-information-war-campaign-6524734
Title Image Courtesy:https://www.tes.com/lessons/&mapsofworld.com
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by the author do not necessarily reflect the views of the Government of India and Defence Research and Studies